* This article is brought to you by GreenLearning and Direct Energy.
Knowing how to read an electricity bill is not only important but it opens the door to understanding how we can help the planet by conserving energy. By reading and interpreting an electricity bill properly, one will be able to adopt behaviour changes to conserve energy, lower one’s carbon footprint, and reduce GHGs, all of which can lead to huge savings. You might be wondering how all of this might be relevant for educators and students.
Firstly, teaching students how to read the electricity bill is an important life skill. It allows students to understand energy better and see how they can make a positive impact for the environment through conservation. In this article, we discuss the importance of this skill and its practical application towards helping students conserve energy at school or home both in Ontario and Alberta. Keep reading for additional tips and tricks you can use for introducing young learners to energy efficiency and conservation. This learning also cuts across subjects such as math, science and engineering.
Why conserve energy? There are a few reasons why you might want to do this. It is obvious that cutting down on how much energy you use can lower your carbon footprint. Using high volumes of electricity produces a lot of greenhouse gasses which negatively impact the environment. Aiming to conserve energy will not only benefit the planet, it will also help you save money. In order to understand how conservation and savings work, having some scientific knowledge about energy terminology is key, such as units of measurement associated with the electricity bill.
Quick Tip: Our Energy Revealed resource called Knowing Energy: Stair Climb is a bundle of learning guides and videos that can help you in understanding the concepts of energy and power with their associated units and terms. It will also help you conserve energy at school.
If you have ever received an electricity bill, you may have noticed that it often uses the acronym kWh. This stands for kilowatts-hour, and is a way to measure the amount of electricity used in an hour. The electricity provider uses this number to calculate how much to charge you on your electricity bill. For example if they charge 0.1510 per kWh and you use 300 kWh a month you would be charged $45.30 for the electricity used.
You may be asking yourself how your electricity usage is calculated. First you need to know how much power your devices use. A watt (W) is the unit used to measure the flow of electrical power. A kilowatt (kW) is 1,000 watts. To find kWh you need to know how much power a device uses and how long it is used for.
The formula for this is kWh = (watts x hours) / 1000. For example if you use a 2000W hair dryer for an hour you would use 2kWh of electricity. Use our Energy Calculator to easily calculate how much kWh devices us, the costs and GHG produced.
Understanding how our devices consume electricity can help us make better decisions on what we purchase and can save us money in the long run. Choosing more energy efficient devices can help us cut down on our electricity usage.
Reading Your Electricity Bill: Ontario vs. Alberta
Although Ontario and Alberta are in the same country, our electricity bills look very different. The bills in each region will vary as there will be different fees and electricity providers. Below, we’ve attempted to outline the components of each bill for your knowledge and learning.
Ontario Electricity Bill

At the top of your bill you should have your account number, amount due and due date. The rest of the electricity bill will outline the different fees that occur from your electricity usage. Here’s a list of electricity charges that should appear.
Electricity Supply Charge is the amount of electricity you use over the course of your billing period. Listed next to it will be the rates and the amount of electricity you used. This allows you to see how they calculate your electricity fee. Most homes in Ontario use a time of use (TOU) price system. This means that depending when you use the electricity you will be charged a differing rate. The difference is due to how much electricity is being used at that time of day. For example On-Peak is usually when most people use electricity so at this time of day it costs a bit more.
Delivery is the fee for transporting electricity. In most cases this is a fixed cost
Regulatory Charges are fees that are charged to the customer to cover energy system operation and other expenses.
Tax electricity falls under Harmonized Sales Tax (HST).
Alberta Electricity Bill
Here’s a basic Direct Energy bill that shows some important information about the electricity usages and charges in Alberta. Using the glossary of energy terms, we have outlined some of the details that might show up on your standard electricity bill and their definitions. Refer to the list below for a better understanding of these terms and how to read the document.
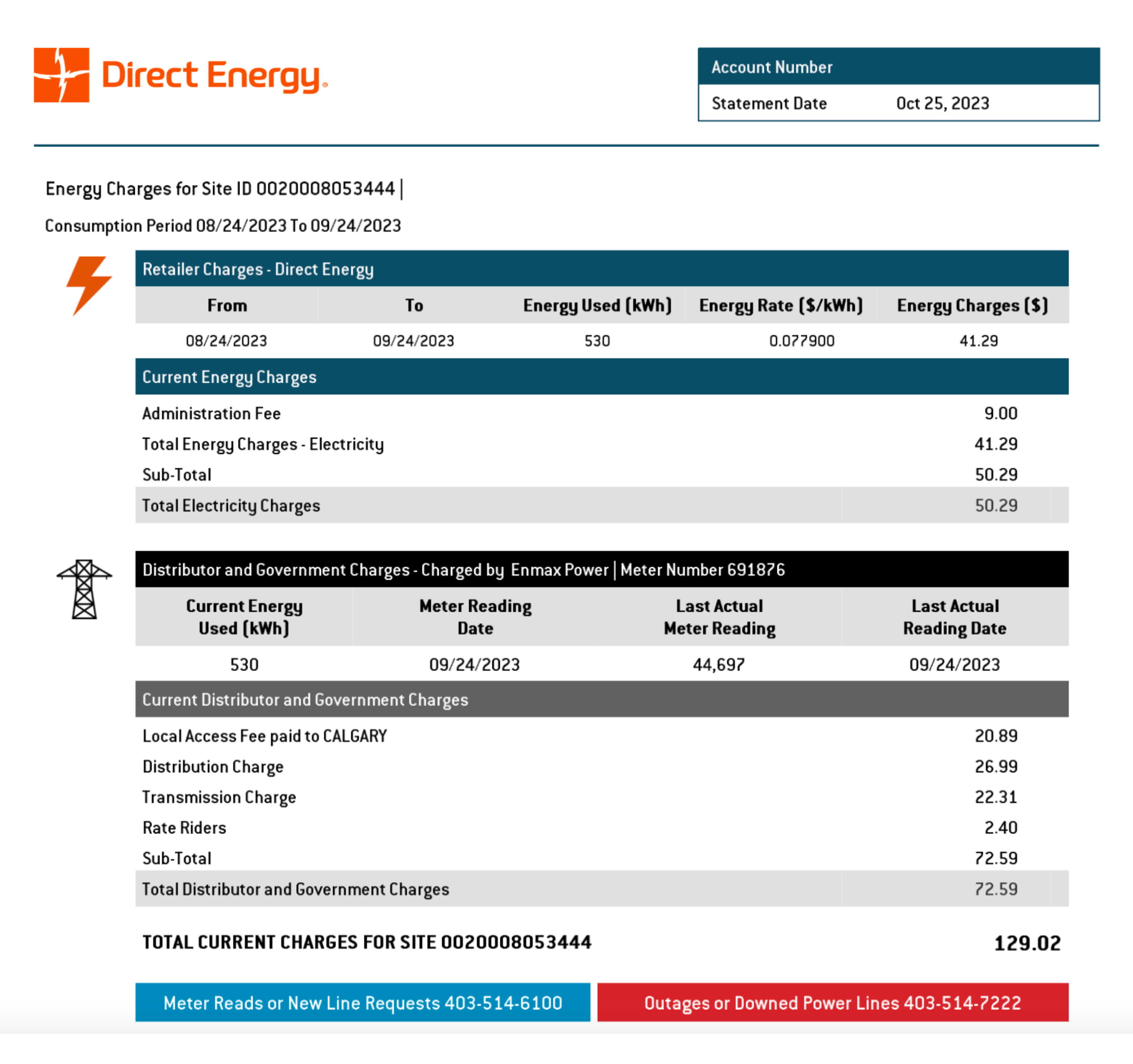
Energy Used (kWh) represents the kilowatt hours of electricity you consumed in the billing period. This can be either an actual or an estimate.
Administration Fee (Fixed) is to cover the costs related to billing you for the electricity and providing customer service.
Cost of Electricity covers the cost of electricity that you used during the billing period.
Distribution Charge (Fixed/Variable) is from your distribution company to recover the operating cost of the lower voltage lines that carry electricity from the transformers to your meter. Distribution and transmission companies set those delivery charges and the Alberta Utilities Commission (AUC), an independent agency, ensures that it is fair and reasonable for the customer. No matter who you choose to buy your energy from, these fees won't change.
Transmission Charge is from your transmission company to recover the costs of owning and operating the high voltage lines that carry electricity to the substation transformers. Distribution and transmission companies set those delivery charges and the Alberta Utilities Commission (AUC), an independent agency, ensures that it is fair and reasonable for the customer. No matter who you choose to buy your energy from, these fees won't change. Watch this video to learn more about what these delivery charges pay for and who sets these fees.
Local Access Fee (LAF) is a surcharge levied by your municipality through your Distributor. It is not approved by the Alberta Utilities Commission. Contact your Distributor, as shown on your energy bill, to find out how this charge is determined.
Rate Rider(s) which are approved by the Alberta Utilities Commission (AUC) enable distribution companies and regulated retailers to recover actual operational costs that are not included in their monthly approved rates.
Tax 5% goods and services tax applies to electricity.
Now that you’ve understood the charges that appear on a standard Alberta electricity bill, you might want to know what kind of energy user you are. Taking Direct Energy’s personality quiz can help you know your consumption habits and then you’ll be better equipped to take measures towards adjusting your usage. Overall, this ensures that you are able to reduce your carbon footprint and make decisions that are better for the environment. Also, be sure to check out our tips below for ways you can save energy in general.
Tips for Saving Energy at School
Small changes can lead to BIG savings! It’s not only good for your wallet but also for the planet. Think about how much better the environment will be because you decided to change the way you relate to energy. If you are feeling optimistic about doing better for the natural world, then check out some or all of these energy savings tips that you can adopt today!
Shut down your computer to save energy.
Lights off! When you're not using the lights in your room, shut them off.
Open your curtains. Having the curtains open lets in sunlight and heat, making your classroom more comfortable.
Reverse your fan blades direction to make your room feel warmer. By rotating the blades to go counterclockwise during the winter, it will push down the warm air throughout the room.
Turn down your thermometer. When you know you won’t be in the room, don't have the thermometer set high.
To learn more energy saving tips, check out GreenLearning’s Energy Revealed program for lessons and activities that are suitable for teaching young people about how to conserve energy and use it more efficiently. Feel free to register for the challenge, which allows students to host a conservation event at school and be in the running to win the grand prize of up to $1,000 for their school community.
References:
“Breaking down Your Ontario Electricity Bill.” EnergyRates.ca,
energyrates.ca/ontario/breaking-ontario-electricity-bill/. Accessed 1 Nov. 2023.


